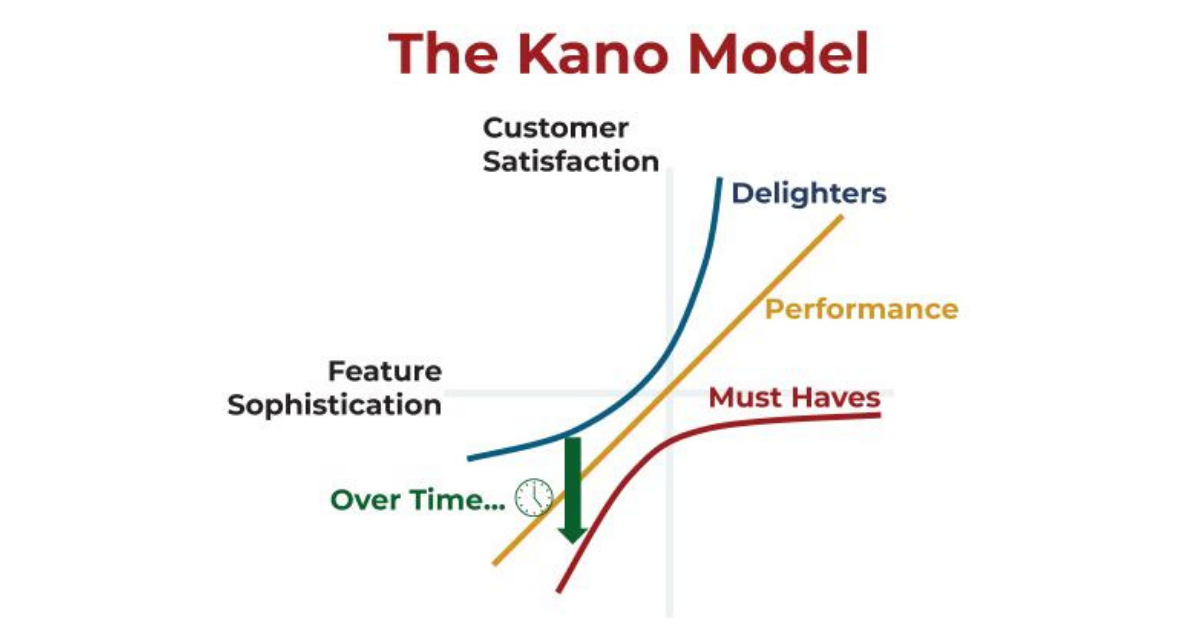
The Kano Model, developed by Professor Noriaki Kano in the 1980s, offers a unique lens through which to view customer preferences and product features. At its core, the model categorizes features based on how they are perceived by customers and their effect on customer satisfaction. This categorization helps product managers and developers prioritize features, ensuring that products not only meet customer needs but also delight and surprise them.
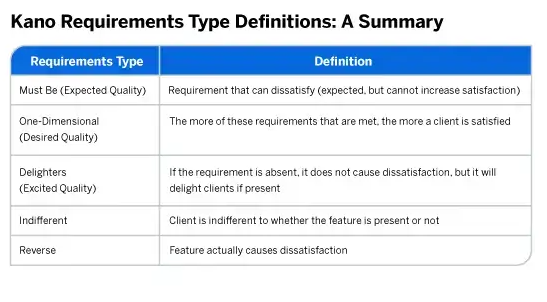
Categories of the Kano Model:
- Basic Needs: These are the features that customers expect. Their absence would cause dissatisfaction, but their presence doesn’t particularly increase satisfaction. Think of them as the minimum requirements for a product to be viable.
- Performance Needs: Features that customers explicitly desire and expect. They are often the features that are promoted and compared in the marketplace. Improving these can lead to increased satisfaction.
- Excitement Needs: These are the delightful surprises that can greatly increase satisfaction when present but don’t cause dissatisfaction when absent. They can be a unique selling point for a product.
- Indifferent Needs: Features towards which customers are neutral. Their presence or absence doesn’t significantly impact satisfaction.
- Reverse Needs: Features that can cause satisfaction when absent and dissatisfaction when present, often because different customer segments have opposing preferences.
Implementing the Kano Model:
To utilize the Kano Model, organizations often survey customers, asking them about the importance of different features and how they would feel if a feature were present or absent. Analyzing these responses can help categorize features into the aforementioned buckets.
Benefits of the Kano Model:
- Prioritization: Helps teams focus on what truly matters to customers.
- Resource Allocation: Ensures that resources are spent on features that will maximize customer satisfaction.
- Strategic Advantage: By focusing on excitement needs, companies can differentiate themselves in the marketplace.
Conclusion:
The Kano Model provides a structured way to think about product features and customer satisfaction. By understanding and categorizing features, organizations can make more informed decisions, ensuring that their products resonate with and delight their customers.